
The electron spin quantum number is unaffected by the values of n, l, and ml. This quantity indicates the orbital angular momentum projected along a specified axis. The total number of orbitals in a subshell, as well as their orientation, is determined by the magnetic quantum number. Its value equals the total number of angular nodes in the orbital and is symbolised by the letter ‘l.’ The form of an orbital is described by the azimuthal quantum number (or orbital angular momentum). A bigger value of the primary quantum number denotes a greater distance between the nucleus and the electrons since it indicates the most likely distance between the nucleus and the electrons (which, in turn, implies a greater atomic size). The principal quantum numbers are represented by the symbol ‘n.’ They represent the main electron shell of an atom.

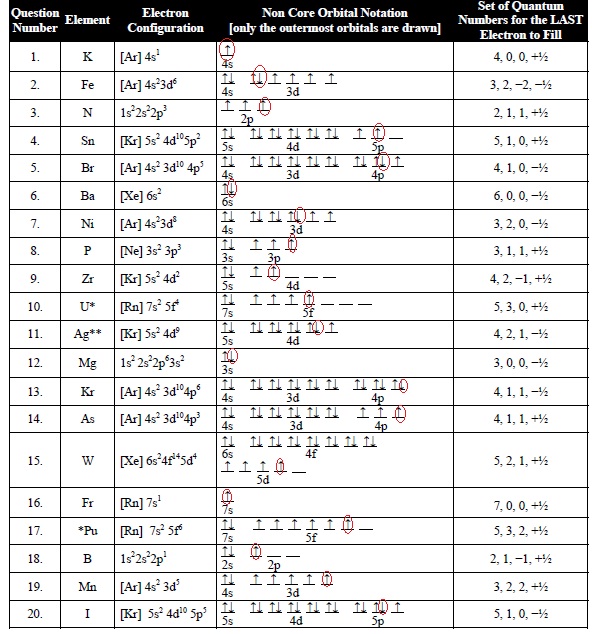
Quantum numbers are the values of the preserved quantities in a quantum system. Quantum numbers are divided into four categories: primary, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin. The collection of numbers used to characterise the location and energy of an electron in an atom is known as quantum numbers. The Schrodinger equation must be satisfied when the quantum numbers of all the electrons in a particular atom are combined together. The route and movement of an electron within an atom may be described using quantum numbers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
